What is EDTA?
EDTA or ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is a common ingredient in skincare and body care products. EDTA helps to improve the foaming of cleansers, soaps, and body washes. Two primary forms of EDTA are frequently used in personal care products, Tetrasodium EDTA and Disodium EDTA. The main difference between tetrasodium EDTA and disodium EDTA is the structure of the molecules and the pH. They two have similar uses in cosmetics and personal care products.
EDTA is included in many hair and skincare products as a preservative, helping to prevent the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds in your skincare product. Preservatives often have a bad reputation in the skincare world, but they help to extend your product’s shelf life and prevent user contamination. Synthetic preservatives also irritate the skin less than some natural preservatives and are less likely to interact with other ingredients in formulations.
EDTA is mainly used as a preservative, but it is also used to improve the foaming abilities of products. This characteristic is why you will often see EDTA in your soaps and cleansers. It is such an effective ingredient that even many natural brands will use it for their formulations as it is hard to substitute.
12 Skincare Ingredients You May Want to Avoid
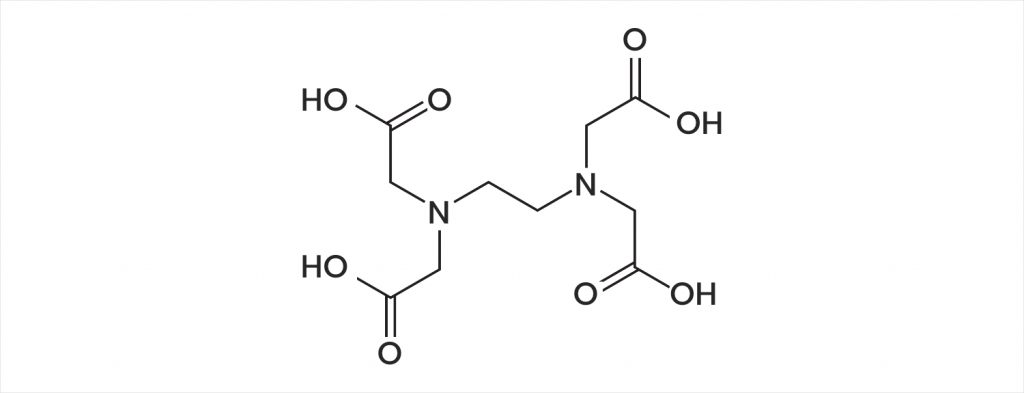
EDTA
the good:EDTA is used as a preservative in skincare products, protecting against the growth of mold, bacteria, and yeast. It also helps products to foam and lather.
the not so good:Can cause some irritation in some people.
Who is it for?All skin types except those that have an identified allergy to it.
Synergetic ingredients:Works well with most ingredients.
Keep an eye on:The two different forms that are used in skincare and body care formulations, disodium EDTA, and tetrasodium EDTA.
Why Is EDTA Used?
EDTA is a water-soluble ingredient used as a chelator. Chelators or chelating agents bind to mineral ions and inactive them. The chelating characteristics give EDTA the ability to work as a preservative and to help products work better in water with a large number of dissolved minerals or hard water.
As a preservative, EDTA works by preventing the growth of biofilms and the outer membranes by inactivation of minerals such as calcium, zinc, and magnesium within the cell. Biofilms are a protective barrier produced by bacteria to protect them from the environment. If these biofilms are unable to be created, bacteria are unable to grow.
EDTA was initially used to reduce the effects of hard water when manufacturing textiles. EDTA improves the foaming and cleansing abilities of products by forming complexes with the calcium, magnesium, and iron present in water. These complexes form and prevent build up on their minerals on the skin or hair.
Besides its uses as a preservative, Tetrasodium EDTA is also valued in skincare applications because of its ability to increase the penetrability of the natural skin barrier and allow deeper penetration by other ingredients. This quality can be especially useful in boosting the effectiveness of certain products by allowing the active ingredients to penetrate deeply, thus producing a more meaningful effect.
Is EDTA Safe?
The safety of EDTA has come under scrutiny in recent times over claims of reproductive toxicity and irritation. These claims are unfounded in the context of skincare and body care products. Both the US Food and Drug Administration, as well as the Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel, have deemed the product to be safe for its indicated uses. In the research conducted to determine the safety of EDTA, it was not found to be carcinogenic or irritating to the skin or eyes.
The claims around reproductive health and irritation come from a small number of studies that investigated the impact of ingredients that bind metals on regular cell activity. Some of the results suggested that EDTA may be weakly mutagenic and that oral exposure to large doses of chelators may affect reproductive health. These studies were conducted with concentrations of chelators outside of the range that would be used in skincare. In terms of the irritation claims, EDTA is not well absorbed through the skin, with very little skin penetration occurring. The Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel, found in their research that EDTA may act as penetration enhancers, helping other ingredients to penetrate deeply into the skin. This is great for improving the penetration of key ingredients but isn’t always good as some ingredients are safer when not significantly absorbed.
Tetrasodium EDTA vs. Disodium EDTA
The two primary EDTA forms that are used in skincare and body care formulations are disodium EDTA and tetrasodium EDTA. These two ingredients have very similar uses in skincare but have some small differences in the way they are used. The main two differences between the two ingredients are that they have a different number of sodium cations; tetrasodium EDTA has four sodium cations, and disodium EDTA has two. This difference affects the pH range which these two ingredients work best at. For tetrasodium EDTA the ideal pH range is 10-11, and disodium EDTA’s ideal pH is from 4-6. This may affect which EDTA you will use in your formulation but doesn’t change the efficacy of the product in any significant way.
References:
Cosmetic Ingredient Review, 2019. ‘ Safety Assessment of EDTA & Salts as Used in Cosmetics, Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel. Finnegan, S & Percival, S, 2015. ‘EDTA: An Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Agent for Use in Wound Care’, Advances in Wound Care, vol. 4, is. 7, pp. 415-421. Oviedo, C & Rodríguez, J, 2003. ‘EDTA: the chelating agent under environmental scrutiny, Química Nova, vol. 26, is. 6.







